Importance of Coenzyme Q10 in nutrient and found throughout the body, especially the heart, liver, kidneys, and pancreas. Our body obtains it through ingested food and by transformation of the vitamins in food.
Table of Contents.
What is and Coenzyme Q10 provide?

The Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is a vitamin-like substance. It will find in every cell of the body. Your body produces CoQ10, and your cells use it to provide energy that your body needs for cell growth and maintenance. It also works as an antioxidant, which protects the body from damage caused by harmful molecules.
CoQ10 is naturally present in small amounts in a wide variety of foods. However, levels are particularly high in organ meats such as heart, liver, and kidney, as well as beef, soybean oil, sardines, mackerel, and peanuts.
The Coenzymes help enzymes work to digest food, and perform other functions of the body, help protect the heart and skeletal muscles
Importance of Coenzyme Q10 Benefits

It is said to help to control heart failure, as well as cancer, muscular dystrophy, and periodontal disease. It is also said to increase energy and speed recovery after exercise. Some people take it to help reduce the effects of some medicines which have effect on the heart, muscles, and other organs.
Heart disease:
The coenzyme Q10 prevents the remaking of heart health by preventing oxidative damage. Coenzyme Q10 deficiency is common in cardiac patients.
High Blood Pressure
39% of patients with high blood pressure have a deficiency of coenzyme Q10. Two studies by a team of Italian researchers between 1992 and 1994 revealed that Coenzyme Q10 supplements reduce blood pressure by up to 10%.
Diabetes
A study conducted showed that diabetic patients taking coenzyme Q10 and vitamin E supplements had fewer complications and damage to the pancreas. An increase in carbohydrate metabolism was detected, which helped control the blood sugar level.
Obesity
In a 1984 Dutch study found that 52% of obese people were deficient in coenzyme Q10. Therefore, raising the level of Coenzyme Q10 in the body can increase the ability to burn fat and lose weight.
Properties of Coenzyme Q10

The coenzyme Q10 is a compound found naturally in every cell of the human body. The alternative name ubiquinone word ubiquitous means “everywhere.” Coenzyme Q10 produces vital energy in the mitochondria, and to the cell where the necessary energy production by the body.
In addition to being a powerful antioxidant, Coenzyme Q10 has many more health benefits. Several experiments demonstrate that coenzyme Q10 has been a useful compound in the prevention of heart injury. It helps in the energy production process of the heart muscles. It also improves the recovery of patients who undergo heart surgery.
Invention by experts says that the importance of coenzyme Q10 in the heart and circulation; they also tell its possible positive effects in the treatment of high blood pressure. Several independent tests and trials are conducting trying to find the link between the compound CoQ10 and the condition of high blood pressure.
Coenzyme Q10 amazingly helps improve conditions for people with high blood pressure disorder, lowers systolic blood pressure by 17mmHg, and diastolic blood pressure by 12mmHg.
Furthermore, Coenzyme Q10 is also considered effective in controlling the condition of diabetic individuals. It is using to control the sugar level of patients with high blood sugar, while also reducing blood pressure. How Coenzyme Q10 lowers the level of blood pressure is the same mechanism as to how antioxidants divert free radicals in the body and preserve nitric oxide to improve the functions of blood vessels.
Importance of Coenzyme Q10 benefits for skin

In the first 20 years of our life, our skin does not face any problem. He is young and radiant. So, This is due to the presence of Coenzyme Q10 in our body. It provides the nutrients that are necessary for our skin to stay healthy.
But once we reach the age of 30, the level of CoQ10 in our body begins to drop. It means that the skin does not receive any nutrients, so aging occurs.
To prevent aging of the skin and to keep it healthy, We can take coenzyme supplements to compensate for the body. This supplement comes in the form of various skin care products, such as creams, to apply directly to the skin.
Harmful free radicals cause skin aging. CoQ10 enzymes are antioxidants that destroy these radicals, thus reducing the speed of the aging process. In addition to this, the vitamin also increases collagen and elastin levels for maintaining the flexibility of the skin.
You can get CoQ10 in foods like bluefish, or foods like meat and poultry products, oils like soy, olive, coconut, sunflower, nuts like peanuts, walnuts, or almonds, fruits like apples, oranges, grapefruits, and vegetables like parsley, broccoli.
Lifestyles are the everyday behaviors and practices that people adopt throughout their lives. When these practices promote the health of individuals, we can speak of healthy lifestyles. It is in these styles of living in health where the significant change will appear.
Coenzyme Q deficiencies 10.

Coenzyme Q 10 is not considering a vitamin since the body can synthesize it. However, a part of this coenzyme is degrades and must be compensated for by dietary intake. The usual intake of coenzyme Q 10 is 5-10 mg and can find mainly in meat, turkey, and fish.
Sometimes the capacity of synthesis of coenzyme Q 10 is diminished, or the requirements are increasing and may be consider to be essential in some situations.
Coenzyme Q 10 deficiency may be genetic in origin. However, the most common causes of coenzyme Q 10 deficiency are:
Increased levels of coenzyme Q 10 and high degradation as a consequence of the physical activity.
- Low intake of coenzyme Q 10 in the diet, for example, vegetarian foods.
- Q10 deficiencies will reduce synthesis as a consequence of other nutrients ( magnesium, selenium, vitamin B6).
- High consumption of vitamin E reduces the uptake of coenzyme Q 10.
- Statins reduce the biosynthesis of coenzyme Q 10.
- Age is one of the leading causes of the reduction of the levels of coenzyme Q 10, and its deficiency will considering to be partly responsible for the manifestations of age.
Also, smoking and in various medical conditions such as cardiovascular, neurological diseases, hypertension, gum disease, infertility, asthma, or immunodeficiency reduces levels of coenzyme Q 10.
The commercially used coenzyme Q 10 is obtained from synthesis from coenzyme Q9 or the extraction of the fermentation product of a type of yeast.
Even though both reduced and oxidized forms can pass from one to the other in the human body, there are different opinions about the best way to supplement coenzyme Q 10. There are different opinions on which form is better to enhance. It would be a way to save the body from transforming into the antioxidant form. However, some authors believe that the ubiquitous form is more stable, comfortable with formulating and storing.
Dose
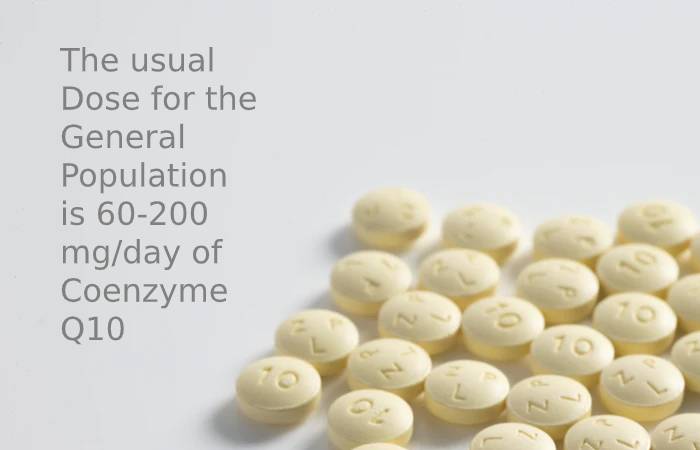
The usual dose for the general population is 60-200 mg/day of Coenzyme Q 10 divides into different treatments throughout the day. However, for Coenzyme Q 10 supplementation to be effective in improving performance, it is necessary to increase the plasma concentration in a sufficient amount in time for the muscles to capture it. To increase the amount of muscle coenzyme Q 10, doses of 200-300 mg daily or even higher treatments will require for at least 4-12 weeks.
Physical activity favors the uptake of coenzyme Q 10 from the plasma to the muscles.
The doses in clinical applications are usually higher, but a specialist should recommend the most appropriate treatment in each case.
Cautions
Coenzyme Q 10 is a nutrient is consider quite safe even in high doses. Gastrointestinal complaints such as nausea, anorexia, or skin rashes have reporting rarely after supplementation with coenzyme Q 10 (less than 1%). When consuming amounts more significant than 100 mg/day, it will recommend dividing the dose into several doses to minimize possible side effects.


